Learning how to import a CSV file into R and RStudio is fundamental for data analysis workflows. This complete guide shows you how to import CSV file in R and import CSV file in R Studio using both the RStudio import CSV graphical interface and the read.csv() function with code-based methods.
Whether you need to load CSV file in R for data cleaning, import CSV to R for statistical analysis, or upload CSV to RStudio for quick exploration, this tutorial covers everything. We'll show you how to read CSV in R, use the read.csv() function effectively, and handle common data import challenges.
In six easy-to-follow steps, you'll master R Studio import CSV workflows and learn how to import CSV data into R efficiently using read.csv() for any project.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure you have R and RStudio installed on your computer. If you haven't installed them yet, follow our step-by-step guide on how to install R and RStudio on Windows, macOS, Linux, and UNIX.
Once done, open up R Studio, and let's get going.
Working with Excel files instead? See our guide on importing Excel files into R.
Method 1: How to Import a CSV File in R Using GUI
Using the GUI in R Studio is a straightforward and convenient way to import a CSV file. Here are the steps to follow:
Step 1: Launch R Studio
Let's start by opening R Studio on your computer.
Step 2: Go to 'Import Dataset'
Look for the Environment pane, usually located on the upper right-hand side. You'll see an Import Dataset dropdown menu. Click on it.
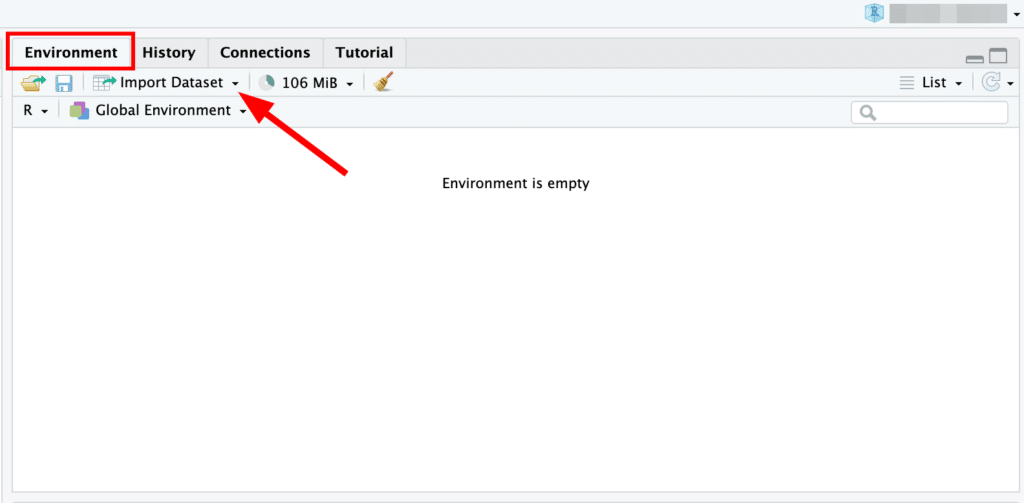 RStudio Environment pane with Import Dataset dropdown menu highlighted.
RStudio Environment pane with Import Dataset dropdown menu highlighted.
Step 3: Choose 'From Text (readr)...'
In the dropdown menu, select the From Text (readr)... option. This will open a file explorer.
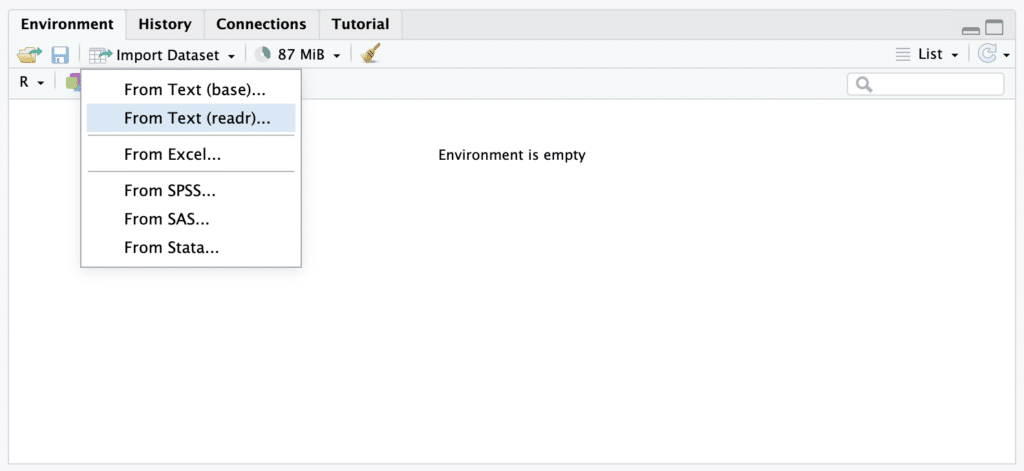 Selecting "From Text (readr)..." option from the Import Dataset dropdown menu in RStudio.
Selecting "From Text (readr)..." option from the Import Dataset dropdown menu in RStudio.
Step 4: Select Your CSV File
Click on the Browse button and navigate to your CSV file in the file explorer, select it, and click Open.
Step 5: Adjust Import Settings
R Studio will open a data import window. Here, you can tweak how R Studio reads your CSV file. You can set things like whether the first row contains the column names or the maximum number of rows to read in.
Step 6: Click on 'Import'
Once you've adjusted the settings to fit your needs, click on the Import button. Your CSV data will be imported into R Studio as a data frame.
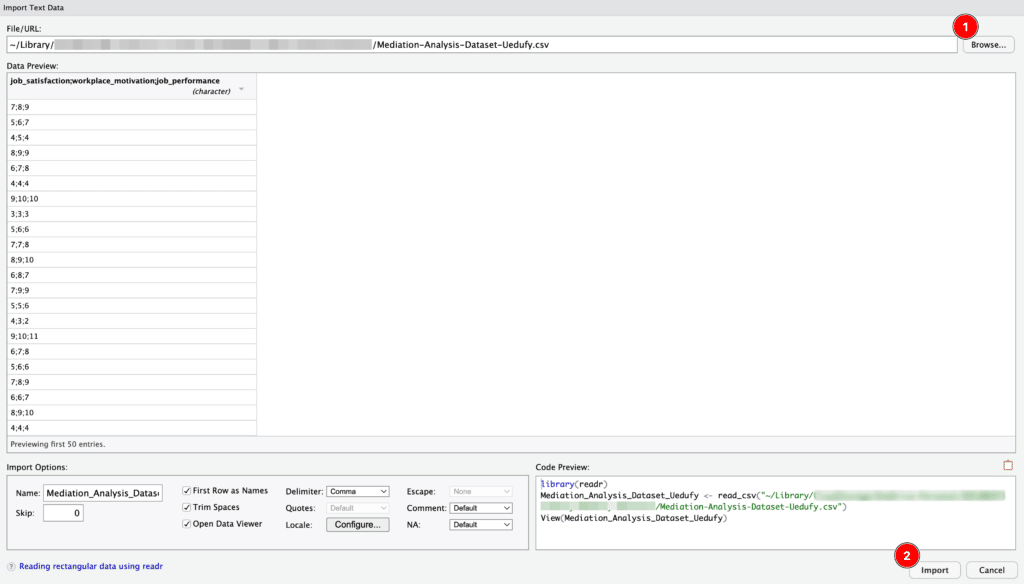 Import Text Data window in RStudio showing CSV data preview and import options.
Import Text Data window in RStudio showing CSV data preview and import options.
Method 2: How to Import a CSV File in R Using Code
If you prefer a more reproducible way of importing your CSV files, or you're working outside of R Studio, here's how you can import a CSV file using code in R:
Step 1: Set Your Working Directory
First, you need to set your working directory to the location of your CSV file. You can use the setwd() function for this:
setwd("/path/to/your/directory")Replace "/path/to/your/directory" with the actual path to your directory.
Step 2: Use read.csv() Function
The read.csv() function is used to import CSV data into R. Suppose our file is named data.csv:
data <- read.csv("data.csv")In this code, data.csv is the name of the CSV file to import, and data is the R data frame where we store the CSV data.
Step 3: Verify the Data
To make sure your data has been imported correctly, you can use the head() function to view the first few rows or the View() function to see the entire dataset:
head(data)
View(data)Step 4: Handle Missing Data
CSV files often contain missing values, which R converts to NA. You can handle these values using various functions like na.omit() to remove rows with NA, or replace() and is.na() to replace NA values:
# Remove rows with NA
data <- na.omit(data)
# Replace NA values with 0
data[is.na(data)] <- 0Step 5: Save the Data
If you want to save your data frame back to a CSV file, you can use the write.csv() function:
write.csv(data, "data_modified.csv")This will save your data frame 'data' to a CSV file named data_modified.csv.
Now you know how to import a CSV file into R both through the GUI in R Studio and by writing code in R. Both methods have their strengths, so choose the one that best fits your needs and comfort level.
Frequently Asked Questions
Wrapping Up
In this comprehensive guide, you've learned how to import CSV files into R using both RStudio's graphical interface and the read.csv() function with code-based methods. Whether you're using RStudio import CSV GUI features or command-line approaches, these techniques will help you load CSV files in R efficiently for your data analysis projects.
The read.csv() function is your essential tool for importing CSV data into R, offering flexibility to handle different delimiters, missing values, and data types. As you become more comfortable with R programming, the code-based approach will give you greater control, reproducibility, and automation capabilities in your workflow.
Need help with other data formats? Check out our guide on importing Excel files into R or learn more about installing R and RStudio on your system.