Generating random numbers in Excel is essential for data analysis, statistical sampling, simulations, and research. Excel provides two powerful built-in functions for creating random numbers: RAND() and RANDBETWEEN().
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about random number generation in Excel, from basic formulas to advanced techniques for creating unique random numbers without duplicates.
Understanding Excel's Random Number Functions
Excel offers two primary functions for random number generation, each serving different purposes:
RAND() Function
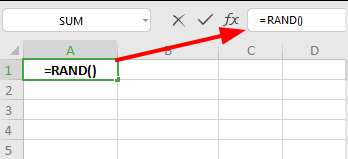
The RAND() function generates random decimal numbers between 0 and 1. Every time your worksheet recalculates (when you make changes or press F9), RAND() produces a new random value.
Syntax:
=RAND()
Key characteristics:
- Returns decimal values (e.g., 0.453892, 0.781234)
- Range is 0 (inclusive) to 1 (exclusive)
- No parameters required
- Automatically recalculates with worksheet changes
Example: To generate a random decimal between 0 and 1, simply enter =RAND() in any cell.
RANDBETWEEN() Function
The RANDBETWEEN() function generates random integer numbers within a specified range. This function is ideal when you need whole numbers for sampling, simulations, or random selections.
Syntax:
=RANDBETWEEN(lower_value, upper_value)
Parameters:
lower_value(the smallest integer you want to generate)upper_value(the largest integer you want to generate)
Key characteristics:
- Returns whole numbers only
- Both bounds are inclusive
- Requires two parameters
- Recalculates automatically
Example: =RANDBETWEEN(1, 100) generates a random integer between 1 and 100 (inclusive).
How to Generate Random Integers with RANDBETWEEN
The RANDBETWEEN function is the most straightforward method for generating random whole numbers in Excel.
Step 1: Select Your Cell
Click on the cell where you want the random number to appear.
Step 2: Enter the Formula
Type the RANDBETWEEN formula with your desired range. For example:
=RANDBETWEEN(10000, 100000)
This formula generates a random integer between 10,000 and 100,000.
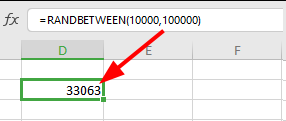
Step 3: Press Enter
Excel will immediately generate a random number within your specified range.
Step 4: Copy to Multiple Cells
To generate multiple random numbers:
- Select the cell containing your formula
- Click and drag the fill handle (small square in the bottom-right corner) down or across
- Excel will generate a new random number for each cell
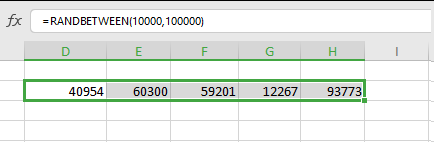
Important note: RANDBETWEEN generates numbers that may repeat. If you need unique random numbers without duplicates, see the advanced techniques below.
How to Generate Random Decimals with Custom Ranges
While RAND() generates numbers between 0 and 1, you can easily scale this to any range using simple arithmetic.
Generate Random Decimals Between Any Two Numbers
To generate random decimal numbers between any minimum and maximum values, use this formula:
=RAND() * (max - min) + min
Example: To generate random decimals between 50 and 100:
=RAND() * (100 - 50) + 50
This produces values like 67.483, 82.194, 55.872, etc.
Generate Random Integers Using RAND and INT
You can also use RAND() combined with INT() to create random integers:
=INT(RAND() * (max - min + 1)) + min
Example: Random integers between 1 and 10:
=INT(RAND() * 10) + 1
How to Generate Unique Random Numbers (No Duplicates)
When conducting random sampling or creating unique identifiers, you need random numbers without repetition. Excel doesn't have a built-in function for this, but you can achieve it using a combination of RAND() and RANK.EQ().
Method 1: Using RAND() and RANK.EQ()
This technique generates a unique ranking from random decimal numbers.
Step 1: Create a helper column with RAND() values
In column A, starting from A1, enter:
=RAND()
Drag this formula down for as many unique numbers as you need (e.g., 10 rows for 10 unique numbers).
Step 2: Use RANK.EQ() to create unique integers
In column B, starting from B1, enter:
=RANK.EQ(A1, $A$1:$A$10)
This formula ranks each random value, creating unique integers from 1 to 10.
Step 3: Copy values and delete helper column
- Copy column B
- Paste as values (Paste Special > Values)
- Delete column A
You now have unique random numbers from 1 to your specified range.
Method 2: Using RANDARRAY() (Excel 365 and Later)
If you have Microsoft 365 or Excel 2021+, the RANDARRAY() function offers a simpler approach:
=RANDARRAY(rows, columns, min, max, TRUE)
Parameters:
rows(number of random numbers to generate)columns(typically 1 for a single column)min(minimum value)max(maximum value)TRUE(generates unique integers without duplicates)
Example: Generate 50 unique random integers between 1 and 100:
=RANDARRAY(50, 1, 1, 100, TRUE)
This single formula creates 50 unique random numbers instantly.
Method 3: Using SORTBY() and SEQUENCE() (Excel 365)
For another Excel 365 approach that generates unique random integers:
=SORTBY(SEQUENCE(n), RANDARRAY(n))
Example: Generate numbers 1 to 100 in random order:
=SORTBY(SEQUENCE(100), RANDARRAY(100))
This creates a randomized sequence of integers from 1 to 100 with no duplicates.
Practical Applications and Examples
Random Sampling for Research
When selecting a random sample from a larger dataset:
- Assign each row a random number using
=RAND()in a helper column - Sort the entire dataset by this random column
- Select the first n rows for your sample
This ensures unbiased random sampling.
Creating Random Test Data
Generate realistic test data for spreadsheets:
Random ages between 18 and 65:
=RANDBETWEEN(18, 65)
Random prices between 99.99:
=RANDBETWEEN(1000, 9999) / 100
Random dates in 2024:
=RANDBETWEEN(DATE(2024,1,1), DATE(2024,12,31))
Then format the cell as a date.
Generating Random Percentages
For random percentages (0% to 100%):
=RAND()
Then format the cell as percentage.
For a specific percentage range (e.g., 20% to 80%):
=RAND() * 0.6 + 0.2
Advanced Techniques and Tips
Freezing Random Numbers (Stop Recalculation)
Random numbers recalculate every time the worksheet changes. To freeze them:
- Select cells containing random number formulas
- Copy (Ctrl+C)
- Right-click > Paste Special > Values
- Click OK
The formulas convert to static values that won't change.
Generating Random Numbers with Decimals in RANDBETWEEN
RANDBETWEEN only produces integers, but you can add decimals:
=RANDBETWEEN(1, 100) + RAND()
This generates numbers like 47.638, 82.193, etc.
For specific decimal places (e.g., two decimals):
=ROUND(RANDBETWEEN(1, 100) + RAND(), 2)
Weighted Random Number Generation
To generate random numbers where certain values are more likely:
Create a probability distribution table, then use RAND() with VLOOKUP() or INDEX/MATCH to select values based on cumulative probabilities.
Avoiding Common Errors
Error: #NUM!
- Cause: In RANDBETWEEN, the lower_value is greater than upper_value
- Solution: Ensure lower_value ≤ upper_value
Numbers Keep Changing
- Cause: Excel recalculates random functions automatically
- Solution: Convert formulas to values using Paste Special
Getting Duplicate Numbers
- Cause: RANDBETWEEN allows repeats by design
- Solution: Use RANK.EQ() method or RANDARRAY() with TRUE parameter
RAND vs RANDBETWEEN: Which Should You Use?
| Feature | RAND() | RANDBETWEEN() |
|---|---|---|
| Output type | Decimal numbers | Whole numbers (integers) |
| Range | 0 to 1 (fixed) | Any range you specify |
| Parameters | None | Two (min and max) |
| Best for | Probabilities, percentages, scaling | Sampling, selections, counts |
| Duplicates | Extremely unlikely | Can occur |
| Excel version | All versions | Excel 2007 and later |
Use RAND() when:
- You need decimal values
- Working with probabilities or percentages
- Creating custom formulas for specific distributions
Use RANDBETWEEN() when:
- You need whole numbers
- Selecting random items from a list
- Simulating dice rolls, lottery numbers, or similar scenarios
Google Sheets Compatibility
Both RAND() and RANDBETWEEN() work identically in Google Sheets, so these techniques apply to both Excel and Google Sheets users. The syntax and behavior are the same across both platforms.
Comparison Table: Methods for Generating Random Numbers
| Method | Type | Range | Duplicates? | Excel Version | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAND() | Decimal | 0 to 1 | Very rare | All | Easy |
| RANDBETWEEN() | Integer | Custom | Yes | 2007+ | Easy |
| RAND() + INT() | Integer | Custom | Yes | All | Medium |
| RAND() + RANK.EQ() | Integer (unique) | 1 to n | No | All | Medium |
| RANDARRAY() | Integer or Decimal | Custom | Optional | 365/2021+ | Easy |
| SORTBY() + SEQUENCE() | Integer (unique) | 1 to n | No | 365/2021+ | Medium |
Frequently Asked Questions
Wrapping Up
Generating random numbers in Excel is a fundamental skill for data analysis, statistical sampling, simulations, and research. Whether you need simple decimal values with RAND(), whole numbers within a specific range using RANDBETWEEN(), or unique random numbers without duplicates using RANDARRAY() or the RANK.EQ() method, Excel provides powerful tools for every scenario.
The key is choosing the right function for your needs. Use RAND() for probabilities and percentages, RANDBETWEEN() for quick integer generation, and RANDARRAY() (if you have Excel 365) for advanced array operations with unique values. Remember that random numbers recalculate automatically, so freeze them using Paste Special > Values when you need static data.
With the techniques covered in this guide, from basic random number generation to advanced methods for creating unique sequences, you now have everything you need to handle random number generation in Excel efficiently and effectively.
References
- Microsoft. (2024). RAND Function - Excel. Microsoft Support Documentation.
- Microsoft. (2024). RANDBETWEEN Function - Excel. Microsoft Support Documentation.
- Microsoft. (2024). RANDARRAY Function - Excel. Microsoft Support Documentation.
- Walkenbach, J. (2023). Excel 2024 Bible. Indianapolis: John Wiley & Sons.